What is Bird’s-Eye View Perception and BEVFusion?
Bird’s-eye view (BEV) perception is a critical technology in autonomous driving. It enables a vehicle to understand its surroundings from a top-down perspective, much like a map view. BEVFusion is a highly complex perception framework that integrates data from both lidar and cameras. It features a transformer-based image backend, a lidar backbone utilizing 3D convolutions, and a view transform module (BEVPool) that is computationally intensive. These complexities pose significant challenges in model deployment and inference, necessitating the use of TensorRT for optimizing certain modules and writing CUDA code directly for others. Nvidia provides an excellent example solution for this process. Below is a summary of Nvidia’s deployment process for BEVFusion.
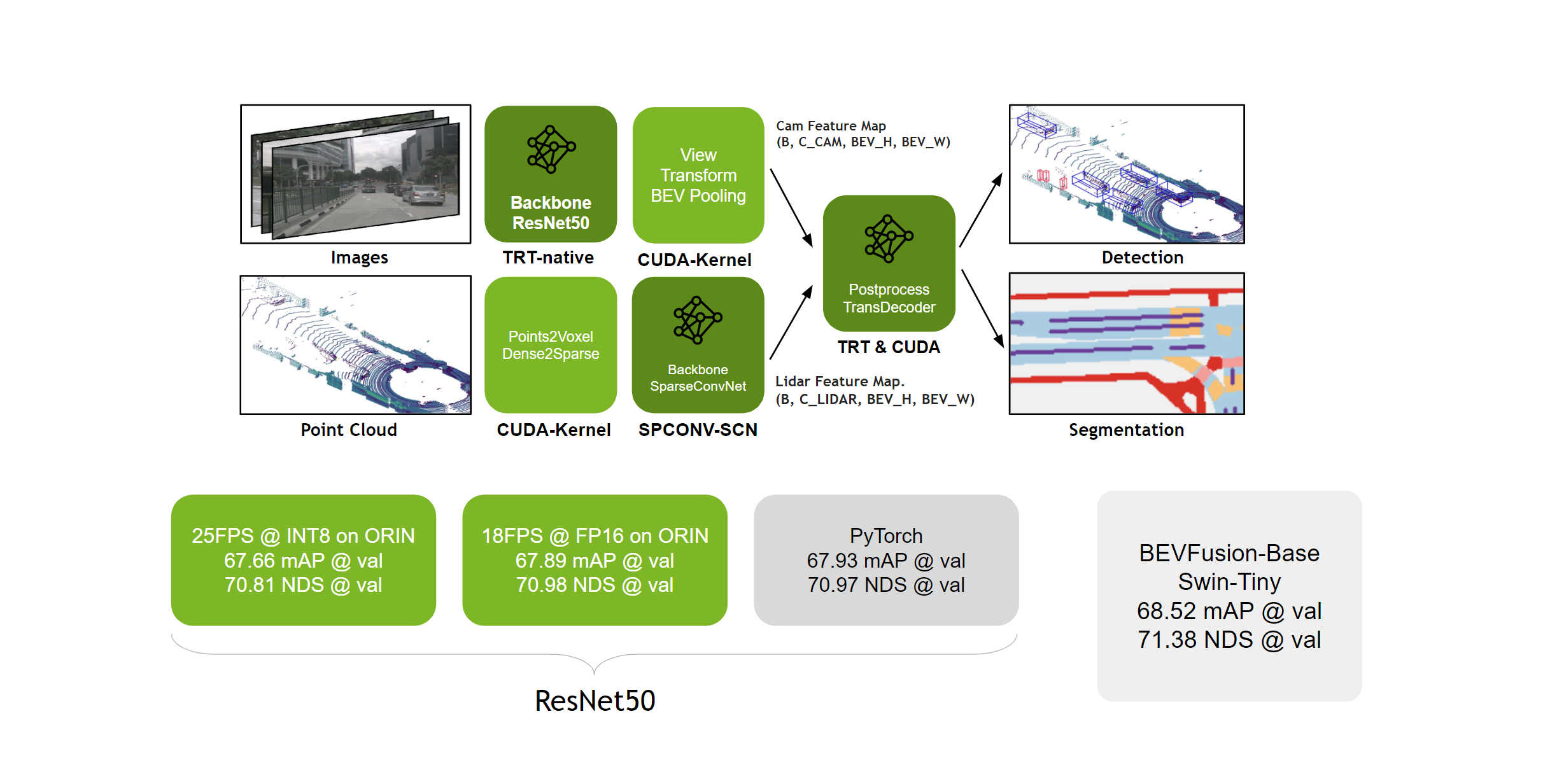
Technical Details about BEVFusion Deployment
1) Quatantation
Since the BEVFusion contains both cuda and tensorrt, the quantization is done by Torch-Quantization instead of by TensorRT directly. Here is the quantization detail:
- Activation value quantization: int8 per-tensor
- Weight quantization: int8 per-channel
- Head quantization: float16
- Calibration Method: MSE
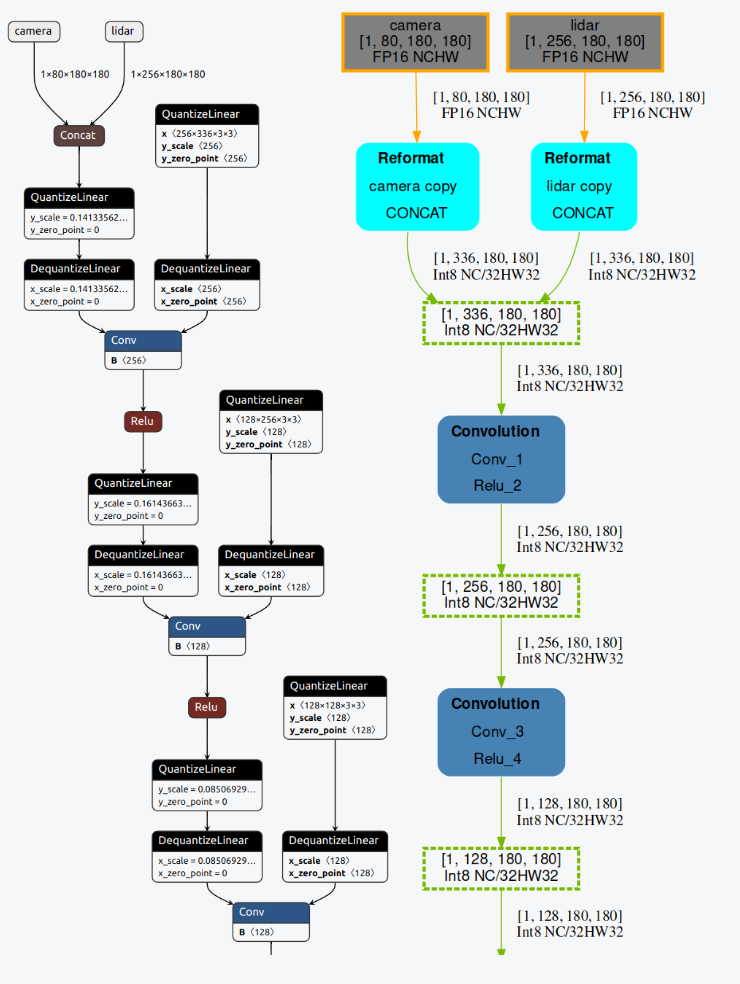 “Left: ONNX graph, Right: TensorRT Engine graph”
“Left: ONNX graph, Right: TensorRT Engine graph”
2) Sparse Convolution Network (SCN)
Both ONNX and TensorRT do not support sparse convolution, making it impossible to deploy the model directly. For ONNX export, we need to use a hook technique to capture the forward function and register the sparse convolution as a custom operation. The exported model is as follows:
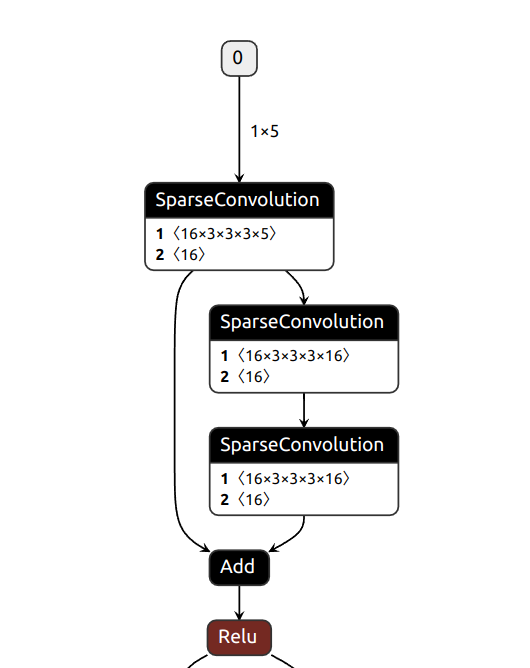 “Sparse Convolution ONNX”
“Sparse Convolution ONNX”
After exported the model to ONNX format, we need to build a engine to excute the model. However, the ONNX model with sparse convolution is not supported by TensorRT. we need to use 3DSparseConvolution tiny engine as a alternative to build a forward function for the sparse convolution layer.
3) View Transformation from camera to BEV space(BEVPool)
BEVFusion’s core component is a view transformation module (BEVPool). This module takes the information captured by the cameras and translates it into a bird’s-eye view (BEV), which is the same perspective used by the lidar sensor. This allows the system to combine data from both sources seamlessly. The view transformation module consists of three steps: Lift, Splat, and Shoot.
Lift: Camera features are “lifted” from the 2D image plane into 3D space using depth estimation. This is often done by predicting depth probability distributions for each pixel.
Splat: The lifted 3D features are then “splatted” or projected onto the BEV grid. Each feature contributes to multiple BEV cells based on its depth uncertainty. This accounts for potential errors in depth estimation.
Shoot: Finally, the features within each BEV cell are aggregated, creating a dense representation of the scene from the bird’s-eye perspective.
The optimization is focuing on speed up the splat and shoot part.
Grid Association Precomputation (Splat)
We assume the camera and lidar’s relative pose is constant, so we can precompute the grid association between the camera and BEV grid. This precomputation is done in initialization and is stored in a lookup table. During inference, we can directly access the lookup table to find the corresponding BEV grid for each camera pixel. This avoids the need for expensive grid association calculations during inference.
Interval Reduction (Shoot)
The next step is then to aggregate the features within the BEV grid. We assign a GPU thread to each grid that calculates its interval sum and writes the result back. This kernel removes the dependency between outputs
and avoids writing the partial sums to the DRAM. The CUDA implementation of the interval reduction is as follows:
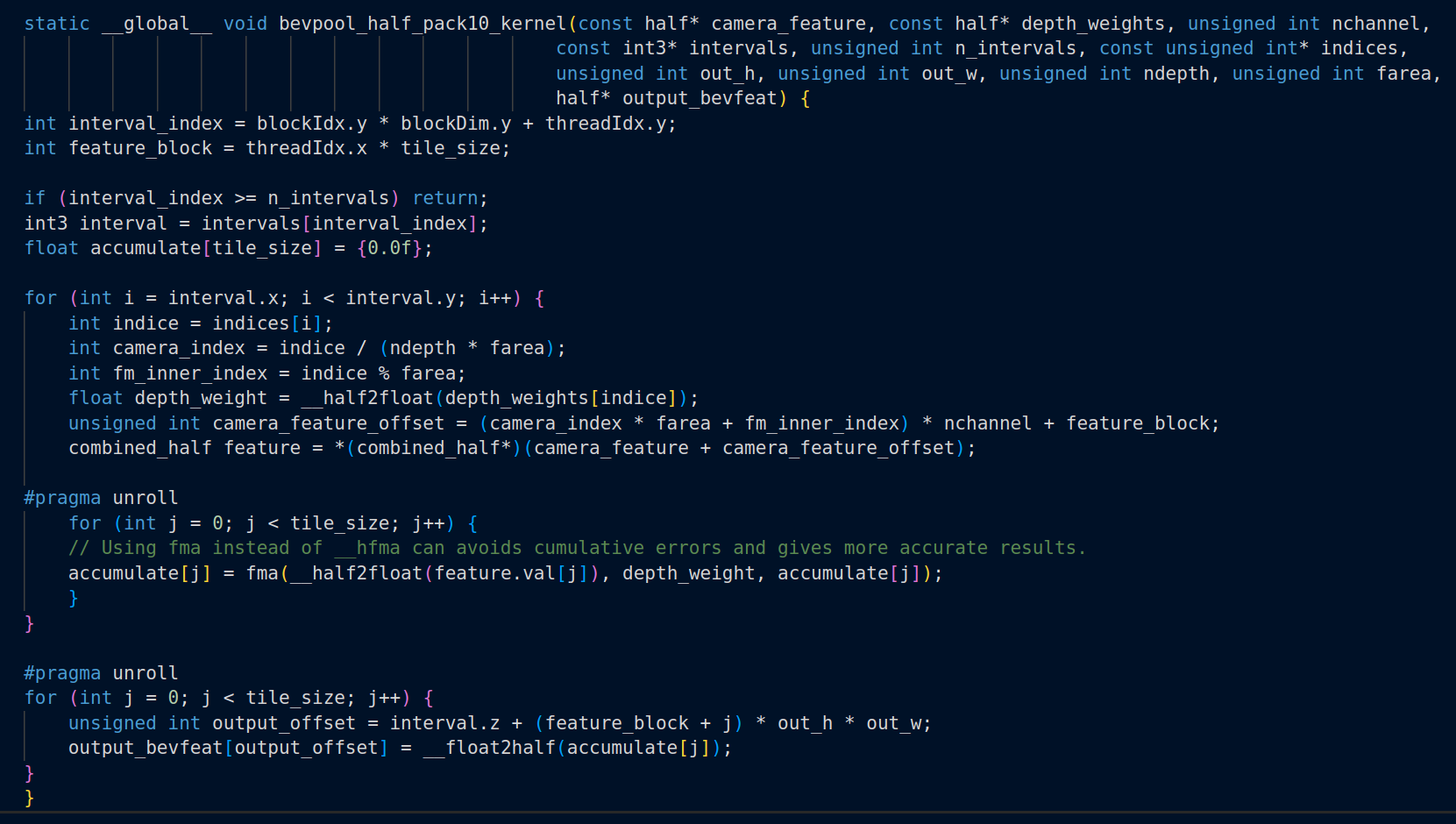 “CUDA implementation of Interval Reduction”
“CUDA implementation of Interval Reduction”
Demo
I deployed BEVFusion on my laptop with a 4060ti GPU and built it as a ROS node. The inference speed of BEVFusion is very fast, achieving 15ms per frame. Below is a simple demo of BEVFusion in RViz.
“Real-Time 3D Object Detection with BEVFusion in Rviz(click to play)”
References:
BEVFusion Paper
BEVFusion CUDA Deployment
nuScenes Dataset
Towards Viewpoint Robustness in Bird’s Eye View Segmentation