What is Bird’s-Eye View Perception and BEVFusion?
Bird’s-eye view (BEV) perception is a crucial technology in autonomous driving. It gives a vehicle the ability to understand its surroundings from a top-down perspective, much like a map view. This holistic understanding is essential for safe navigation and decision-making.
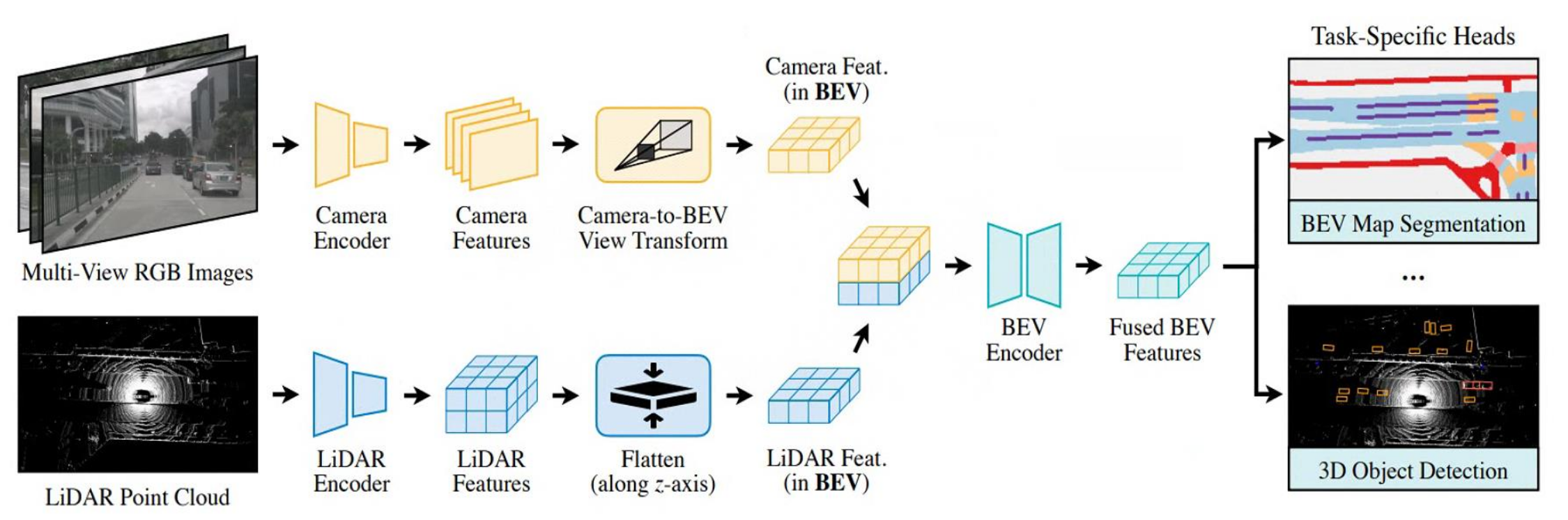
BEVFusion is a powerful framework that combines data from lidar and cameras to achieve highly accurate 3D object detection. This fusion of sensor modalities allows for a more robust and comprehensive understanding of the environment than either sensor could provide alone.
View Transformation from camera to BEV space
The core component of BEVFusion is a view transformation module that transfers camera features into BEV space, enabling the fusion of camera and lidar features in a common representation.The view transformation module consists of three steps: Lift, Splat, and Shoot.
Lift: Camera features are “lifted” from the 2D image plane into 3D space using depth estimation. This is often done by predicting depth probability distributions for each pixel.
Splat: The lifted 3D features are then “splatted” or projected onto the BEV grid. Each feature contributes to multiple BEV cells based on its depth uncertainty. This accounts for potential errors in depth estimation.
Shoot: Finally, the features within each BEV cell are aggregated, creating a dense representation of the scene from the bird’s-eye perspective.
BEVFusion Deployment and Demo
The BEVFusion algorithm can be deployed on an NVIDIA GPU, accelerated by CUDA and TensorRT, and run as a ROS node for real-time object detection. It subscribes to both image and lidar messages as input and publishes object bounding boxes. Here’s a demo showcasing the BEV perception system in RViz:
“Real-Time 3D Object Detection with BEVFusion in Rviz(click to play)”
References:
BEVFusion Paper
BEVFusion CUDA Deployment
nuScenes Dataset
Towards Viewpoint Robustness in Bird’s Eye View Segmentation